Galactorrhea
Galactorrhea is a condition characterized by the inappropriate production of breast milk. This can occur in both women and men, and it is unrelated to the normal milk production associated with childbirth and nursing. Understanding galactorrhea involves exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. This guide provides a detailed overview of this condition to help you understand its implications and management.
What is Galactorrhea?
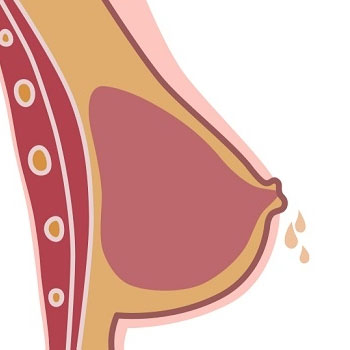
Galactorrhea is the spontaneous flow of milk from the breast, which is not associated with childbirth or nursing. It can affect individuals of any gender and is often a sign of an underlying hormonal imbalance.
Physiology of Milk Production
Normal milk production, known as lactation, is regulated by the hormone prolactin, which is produced by the pituitary gland in the brain. Prolactin levels rise during pregnancy and after childbirth to stimulate milk production in the mammary glands. In the case of galactorrhea, prolactin levels may be abnormally high or there may be an increased sensitivity of the breast tissue to prolactin.
What causes galactorrhea?
Hormonal Imbalances
The most common cause of galactorrhea is an excess of prolactin in the blood, a condition known as hyperprolactinemia. Various factors can lead to hyperprolactinemia, including
- Pituitary Tumors: Prolactinomas, benign tumors of the pituitary gland, can cause excessive production of prolactin
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can lead to increased prolactin levels
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antipsychotics, antidepressants, and antihypertensives, can elevate prolactin levels
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can sometimes increase prolactin production
Other Causes
Apart from hormonal imbalances, galactorrhea can be caused by
- Breast Stimulation: Excessive stimulation of the breasts, whether through clothing or manual manipulation, can trigger milk production
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Kidney problems can affect hormone metabolism, leading to elevated prolactin levels.
- Chest Wall Trauma: Injury or trauma to the chest wall can stimulate the nerves involved in milk production.
What are the symptoms of Galactorrhea?
Primary Symptoms
The main symptom of galactorrhea is the unexpected and persistent discharge of milk from the nipples. This discharge may vary in color from white to yellowish or greenish
Associated Symptoms
Depending on the underlying cause, other symptoms may include
- Irregular Menstrual Periods: Women may experience changes in their menstrual cycle, such as irregular periods or amenorrhea (absence of periods).
- Vision Problems: If a pituitary tumor is present, it can compress surrounding structures, leading to vision disturbances.
- Headaches: Pituitary tumors can also cause headaches due to increased pressure in the brain
- Reduced Libido: Both men and women with elevated prolactin levels may experience a decrease in sexual desire.
How is Galactorrhea diagnosed?
Medical History and Physical Examination
Diagnosing galactorrhea typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. The healthcare provider will ask about the duration and frequency of the milk discharge, any medications being taken, and other associated symptoms
Laboratory Tests
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause, several tests may be performed
- Blood Tests: These measure prolactin levels and check for other hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid function tests
- Pregnancy Test: For women of childbearing age, a pregnancy test is done to rule out pregnancy as a cause of milk production
Imaging Studies
If a pituitary tumor is suspected, imaging studies such as an MRI or CT scan of the brain may be necessary to visualize the pituitary gland and detect any abnormalities
What are the treatment options available for Galactorrhea?
Addressing the Underlying Cause
Treatment of galactorrhea focuses on addressing the underlying cause. Depending on the diagnosis, various treatment options are available
Medications
If medications are causing elevated prolactin levels, adjusting the dosage or switching to an alternative drug may be recommended. For pituitary tumors, medications such as dopamine agonists (e.g., bromocriptine or cabergoline) can reduce prolactin production and shrink the tumor.
Surgery
In cases where a pituitary tumor is large or unresponsive to medication, surgical removal may be necessary.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement
For hypothyroidism-induced hyperprolactinemia, thyroid hormone replacement therapy can normalize prolactin levels.
Managing Symptoms
In addition to treating the underlying cause, managing the symptoms of galactorrhea is important for patient comfort and quality of life. This can include
- Wearing Supportive Bras: To minimize breast stimulation and leakage
- Avoiding Breast Stimulation: Refraining from activities that might stimulate the breasts, such as frequent breast self-exams or excessive physical contact
What complications might arise from this condition?
Prognosis
The prognosis for individuals with galactorrhea largely depends on the underlying cause. For those with medication-induced or stress-related galactorrhea, the condition often resolves once the triggering factor is removed. For those with pituitary tumors, treatment with medication or surgery is usually effective in controlling symptoms and reducing prolactin levels.
Complications
If left untreated, galactorrhea can lead to several complications
- Infertility: Persistent hyperprolactinemia can interfere with ovulation in women, leading to infertility
- Bone Density Loss: Chronic high prolactin levels can reduce estrogen or testosterone levels, potentially leading to decreased bone density and increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Psychosocial Impact: The unexpected and persistent milk discharge can cause emotional distress and impact an individual's quality of life
How can galactorrhea be prevented?
While galactorrhea itself may not always be preventable, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing the condition
- Regular Medical Checkups: Routine health checkups can help detect and manage conditions like hypothyroidism or pituitary tumors early
- Medication Management: Discussing potential side effects of medications with a healthcare provider and making necessary adjustments can prevent medication-induced galactorrhea
- Stress Management: Implementing stress-reducing techniques such as exercise, meditation, or therapy can help prevent stress-induced hormonal imbalances
When to Seek Medical Attention?
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of the following
Persistent or Unexplained Milk Discharge
Any ongoing nipple discharge that is not related to pregnancy or breastfeeding should be evaluated by a healthcare provider
Changes in Menstrual Cycle
Irregular or absent menstrual periods in women could indicate an underlying hormonal issue.
Vision Problems or Headaches
These symptoms, along with galactorrhea, could suggest the presence of a pituitary tumor
Galactorrhea is a condition marked by the inappropriate production of breast milk and is often a sign of an underlying hormonal imbalance. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve the quality of life for those affected. If you suspect you have galactorrhea, consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for proper evaluation and management.
By staying informed and proactive about your health, you can better navigate and manage conditions like galactorrhea. Whether it involves addressing hormonal imbalances, managing stress, or making informed decisions about medications, taking control of your health is key to ensuring well-being.
