Osteoporosis
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more susceptible to fractures. This disease predominantly affects older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, but can occur in men and younger individuals as well. Understanding osteoporosis, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing serious complications.
How can osteoporosis be understood?
Osteoporosis literally means "porous bones." It occurs when the creation of new bone doesn't keep up with the removal of old bone. This imbalance results in bones that are less dense and more fragile. Bones are living tissues that are constantly being remodeled; old bone is broken down by cells called osteoclasts, and new bone is formed by cells called osteoblasts. In people with osteoporosis, this remodeling process is disrupted, leading to a net loss of bone mass.
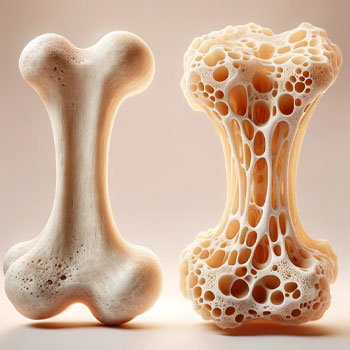
How does Bone Density relate to Osteoporosis?
Bones are living tissues that constantly undergo a process called remodeling, where old bone tissue is broken down and replaced with new bone tissue. This balance between bone resorption (breakdown) and bone formation is crucial for maintaining bone density and strength.
In osteoporosis, this balance is disrupted, leading to a decrease in bone density. The bones lose minerals, such as calcium, more quickly than the body can replace them, resulting in porous and brittle bones.
What leads to the development of osteoporosis?
Several factors can contribute to the development of osteoporosis
Aging
Bone density peaks around the age of 30 and then gradually declines with age. After menopause, women experience a significant decrease in estrogen levels, accelerating bone loss
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormones like estrogen in women and testosterone in men play a vital role in bone health. Lower levels of these hormones can lead to increased bone resorption
Genetics
A family history of osteoporosis can increase an individual's risk of developing the condition.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Inadequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, essential for bone health, can contribute to osteoporosis.
Lifestyle Factors
Sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and poor dietary habits can negatively impact bone health
Medical Conditions and Medications
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, hyperthyroidism, and certain medications, such as corticosteroids, can increase the risk of osteoporosis
What are some indicators of osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is often asymptomatic until a fracture occurs. However, some signs and symptoms can indicate the presence of the disease
- Fractures: The most common symptom, particularly in the hip, spine, or wrist
- Back Pain: Caused by a fractured or collapsed vertebra
- Loss of Height: Gradual loss of height over time due to vertebral compression fractures.
- Stooped Posture: Known as kyphosis, this can result from multiple fractures in the spine
What factors increase the risk of developing osteoporosis?
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing osteoporosis
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 50.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis, particularly postmenopausal women
- Family History: A history of osteoporosis in the family increases risk
- Body Frame Size: Smaller, thinner individuals have a higher risk due to less bone mass.
- Ethnicity: Caucasian and Asian women are at higher risk compared to other ethnic groups
- Hormonal Levels: Low levels of sex hormones increase the risk
- Dietary Factors: Low calcium and vitamin D intake, eating disorders, and gastrointestinal surgeries that affect nutrient absorption can contribute
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle are significant risk factors
- Medical Conditions: Chronic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease, and hyperthyroidism
- Medications: Long-term use of corticosteroids, anticonvulsants, and certain cancer treatments can affect bone density
What methods are used to diagnose osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis can be diagnosed through various methods
- Bone Density Test: The most common test is Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA) which measures bone mineral density (BMD) in the hip and spine.
- Quantitative Ultrasound: This test measures bone density using sound waves, usually at the heel
- CT Scan: Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) provides detailed images and measures bone density
- Lab Tests: Blood and urine tests can help identify underlying conditions contributing to bone loss
How is osteoporosis typically treated?
While there is no cure for osteoporosis, several treatments can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of fractures
Medications
Various medications can help slow bone loss or increase bone formation
- Bisphosphonates: These are the most commonly prescribed drugs and include alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, and zoledronic acid.
- Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs): Medications like raloxifene mimic estrogen's bone-protective effects
- Hormone Therapy: Estrogen therapy can help maintain bone density in postmenopausal women
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Analogues: Drugs like teriparatide stimulate bone growth
- RANK Ligand (RANKL) Inhibitors: Denosumab helps reduce bone resorption
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating healthy lifestyle changes can significantly impact bone health:
- Diet: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through diet and supplements
- Exercise: Weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises improve bone density and balance, reducing the risk of falls
- Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken bones
Fall Prevention
Reducing the risk of falls is crucial for individuals with osteoporosis
- Home Safety: Remove tripping hazards, install grab bars in bathrooms, and ensure proper lighting.
- Vision and Hearing Checks: Regular checks can help prevent falls.
- Assistive Devices: Use canes or walkers if necessary to maintain balance
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a safe exercise program to improve strength and balance.
Pain Management
Over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications can help manage pain from fractures.
How can osteoporosis be prevented?
Preventing osteoporosis involves adopting a bone-healthy lifestyle from a young age
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Ensure sufficient intake through diet and supplements if necessary. Adults need about 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 600-800 IU of vitamin D daily
- Regular Exercise: Engage in weight-bearing activities like walking, running, dancing, and resistance exercises to strengthen bones
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and heavy drinking can decrease bone density
- Bone Density Testing: Regular screenings for those at risk can help detect osteoporosis early.
- Hormonal Balance: Monitor and manage hormone levels, especially in postmenopausal women
- Medication Awareness: Be aware of medications that may affect bone health and discuss alternatives with your doctor
What is it like to live with Osteoporosis?
Living with osteoporosis requires ongoing management to maintain bone health and prevent fractures
- Regular Check-Ups: Keep up with medical appointments and bone density tests
- Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications as directed and discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider
- Stay Active: Continue with safe exercises and activities that strengthen bones and improve balance
- Monitor Nutrition: Maintain a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
- Home Safety: Implement fall prevention measures in your living space
- Support System: Join support groups or connect with others living with osteoporosis for encouragement and advice
Osteoporosis is a serious condition that requires attention and proactive management. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. With the right lifestyle choices, medical care, and preventive measures, individuals can maintain strong bones and reduce the risk of fractures, ensuring a better quality of life.
By staying informed and taking action, you can protect your bone health and live well with osteoporosis. If you suspect you have osteoporosis or are at risk, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for bone health management.
